Summary
Startup founders are like chefs in a kitchen—they all want to cook up success, aiming for long-term growth, whether through an IPO or a tasty acquisition. To get there, many whip up external funding.
Understanding "pre-money vs post-money" is crucial when dealing with venture capital (VC). With VC funding on the rise by 15% annually, mastering these terms is crucial to nailing negotiations.
Key Takeaways:
Pre-money valuation is a company's worth before any new investment enters.
Post-money valuation reflects a company’s value after receiving external investment funds.
Investors prefer pre-money valuations for clarity before new funding is introduced.
Want long-term startup success? spectup helps startups with profound industry insights, anticipating future trends and tackle challenges dynamically to startups needs.
Let's dig into why pre-money and post-money matters.
What is Pre-money Valuation?
Ever wondered how investors decide the worth of a company before they even invest a dime?
That's where pre-money valuation comes in.
Imagine you’re buying a pizza. You’d want to know how big it is before deciding how many friends to share it with, right? Pre-money valuation is a bit like that—it’s the estimated value of a company before any new investment (or dough) is added.
Let’s say you’re an investor looking to buy a slice of the company. The pre-money valuation helps you figure out how much each slice (or share) costs. Think of it like a price tag on a slice of that pizza.
If the company is valued at $7.5 million and there are five million slices (shares) available, each slice would cost you $1.50. Simple math, right?
But what happens after you’ve invested your money? The total value of the pizza (company) grows. This new value, after your investment, is called the post-money valuation. So if you throw in $2.5 million, that pizza is now worth $10 million. You’d own a quarter of that pizza, which sounds pretty satisfying.
The calculation might seem a bit dry, but it’s crucial. Pre-money valuation is calculated before investment, using fully diluted capitalization. You take the pre-money valuation and divide it by the number of fully diluted shares. This number gives investors a clear picture of what they’re getting into.
It’s all about knowing the worth of something before you add your share. Understanding pre-money valuation is key to making smart investment choices.
Remember, it’s not just about numbers—it’s about making informed decisions that could lead to a bigger and better pizza.
To learn more about making the most out of your pre-seed funding round, check out this resource: How to Make the Most Out of Your Pre-Seed Funding Round.
What is Post-money Valuation?
Picture your company as a growing tree. It starts as a small sapling (pre-money valuation), but after some nurturing—like an investor’s cash infusion—it becomes a full-grown tree (post-money valuation). That transformation is key to understanding post-money valuation.
Post-money valuation comes into play when a company raises funds through preferred stock. Let’s say a company is worth $7.5 million before getting any new investment. After investors put in $2.5 million, the company’s value jumps to $10 million. That $10 million is the post-money valuation.
But there’s more to the story. Post-money valuation considers new investments and discounted cash flow. Some companies also have convertible securities like SAFEs (Simple Agreements for Future Equity) or convertible notes. These convert into shares during the financing round.
Imagine there’s an extra $1 million in these convertibles. The functional pre-money valuation then drops to $6.5 million, changing the share price. Instead of each share being worth $1.50, it’s now $1.30.
Investors look closely at post-money valuation. It tells them what percentage of the company they’ll own after the deal. In our example, the $2.5 million investment still buys 25% of the company, even with those convertibles in the mix. Understanding post-money valuation helps investors and founders make smart decisions. It’s not just about numbers—it’s about knowing how the pieces fit together.
Pre-Money / Post-Money AI Calculator
We've created this tool to help founders like ou calculate your valuation easy and straightforward with our tool. Let us know if it's working (or not working).
Pre-money vs Post-money Valuation – What is the Difference?
When raising funds, understanding the difference between pre-money and post-money valuation is crucial. It’s like knowing the price of a cake before and after adding the icing. Pre-money valuation is the value of a company before new investments, while post-money valuation is the value after the investment.
Let’s explore the key differences.
Definition
Pre-money valuation is the value of a company before it getsnew investment. It’s like knowing the worth of a car before any upgrades.Post-money valuation is the value after the investment comes in. It’s the totalvalue with the upgrades included.
Calculation
Calculating pre-money valuation is straightforward. You lookat the company’s current worth without adding any new money. Post-moneyvaluation is different. You add the new investment to the pre-money valuation.So, if a company is worth $7.5 million before and gets a $2.5 millioninvestment, the post-money value is $10 million.
Impact on Share Price
Pre-money valuation helps set the price per share. It tellsyou what each piece of the company is worth before new money changes the game.Post-money valuation impacts the ownership percentage. After the investment,the value is higher, but so is the number of shares.
Use in Negotiations
Pre-money valuation is key in early talks. It sets the stagefor how much the company is worth before any deal is made. Post-money valuationis where the rubber meets the road. It shows how much of the company theinvestor will own after the deal is done.
Relevance of Convertibles
Pre-money valuation doesn’t worry about convertibles likeSAFEs or notes. It’s all about the company’s current worth. Post-moneyvaluation, however, includes those convertibles. They can lower the share pricebecause they add more shares to the mix.
Calculating Pre-Money and Post-Money Valuations
Now, let’s move on to the valuation part with an example of pre-money vs post-money. For background information, it's important to understand how investors make investment decisions.
How to Calculate Pre-money Valuation?
Understanding how to calculate a company's pre money value can seem like cracking a code, but it's pretty straightforward once you get the hang of it. Let's break it down.
First, grasp the basics. Pre-money valuation is the value of a company before it receives any new investment. It’s like figuring out the worth of a house before you decide how much you’ll spend on renovations.
To find this figure, you need to know the post-money valuation. This is the company's value right after the investment is made. The formula to find the pre-money valuation is:
Pre-money valuation = Post-money valuation - Investment amount
Let’s say a company’s post-money valuation is $30 million, and it just secured a $3 million investment. Using the formula, the pre money calculation would be:
$30 million - $3 million = $27 million
So, the company’s value before the new funds came in was $27 million.
Knowing the pre-money valuation helps you figure out the per-share value. To do this, divide the pre-money valuation by the total number of outstanding shares. For example:
Per-share value = Pre-money valuation ÷ Total number of outstanding shares
By following these steps, you get a clear picture of a company’s worth before and after new investments. It’s all about simple math and understanding the timing of when money is
How to Calculate Post-money Valuation?
Calculating post money value might sound tricky, but it’s straightforward. Imagine you’ve got a lemonade stand. If you get $3 in exchange for 10% of the stand, you can figure out how much the stand is worth after the deal.
Here’s the formula to get the post-money valuation:
Post-money valuation = Investment amount ÷ Percentage received
For instance, if an investor puts in $3 million and gets 10% of the company, you’d calculate it like this:
$3 million ÷ 10% = $30 million
So, the post-money valuation of the company is $30 million. This means the company is valued at $30 million right after the $3 million investment.
Keep in mind, the company wasn’t valued at $30 million before the investment. The new cash inflow bumps up its value by the amount invested. Simple math gives you a clear snapshot of the company’s worth post-investment.
Which Valuation is Used More?
When it comes to valuing a company, pre-money valuation often takes the spotlight.
Why?
Investors like it because it’s straightforward and helps them figure out the price per share before any new money comes in.
With pre-money valuation, you know exactly what each share costs before the investment. This clarity helps investors decide how much they want to put in. If a company’s pre-money valuation is $20 million and they’re raising $5 million, the post-money valuation will be $25 million.
Post-money valuation can be trickier. It depends on the final size of the investment round, which might change as investors adjust their offers. This uncertainty makes pre-money valuation the go-to choice. It keeps things simpler and more predictable for everyone involved.
Do Pre & Post-Money Affect You Differently?
Understanding pre- and post-money valuations can be a game changer for founders. Both terms measure a company’s worth but at different times.
Pre-money valuation looks at your company’s value before any new investment comes in. Think of it as the value of your home before you start renovations. You may use various methods to estimate this, but it can involve some guesswork.
On the flip side, post-money valuation reflects your company's worth after the investment is added. It’s like knowing your home’s value right after renovations are complete. This valuation is often simpler for investors because it’s a clear snapshot after all funding is in place.
For you as a founder, understanding both valuations is crucial. Pre-money valuation affects how much equity you’ll give away before the investment, while post-money valuation determines the overall value of your company afterward. Both impact your ownership stake and how much control you maintain.
Why Are Pre-Money and Post-Money Valuations Important for Startups?
Pre-money and post-money valuations are essential for startups for several reasons.
Ownership Percentage: Determines how much control and business ownership investors will have.
Financial Worth: Provides a clear view of the startup's value for assessing investment profitability.
Investment Attraction: Helps avoid overvaluation or undervaluation issues that could impact funding.
Growth Benchmark: Allows startups to track financial progress and make informed future decisions.
Funding Pitch: Essential for presenting an accurate financial picture to attract investors.
Startup valuations are complex and require a deep understanding of financial modeling. spectup provides valuable insights and support to help startups accurately determine their pre-money and post-money valuations.

How do investors use pre-money and post-money valuations to make investment decisions?
Investors use pre-money and post-money valuations to make investment decisions by evaluating the potential return on their investment and the risks associated with the startup. The startup or company's valuation is critical in determining the investor's equity stake in the company, which directly affects their potential return on investment.
Angel investors want to ensure that they are not overpaying for their equity stake and that the startup has a viable business model and growth potential.
Lead investor also uses pre-money and post-money valuations to evaluate the startup's financial stability and the potential risks associated with the investment. A high valuation may signal to investors that the startup is overvalued, while a low valuation may indicate that the startup is struggling.
Additionally, investors may evaluate the startup's market potential, industry trends, and competition to determine if the investment is worth their time and resources.
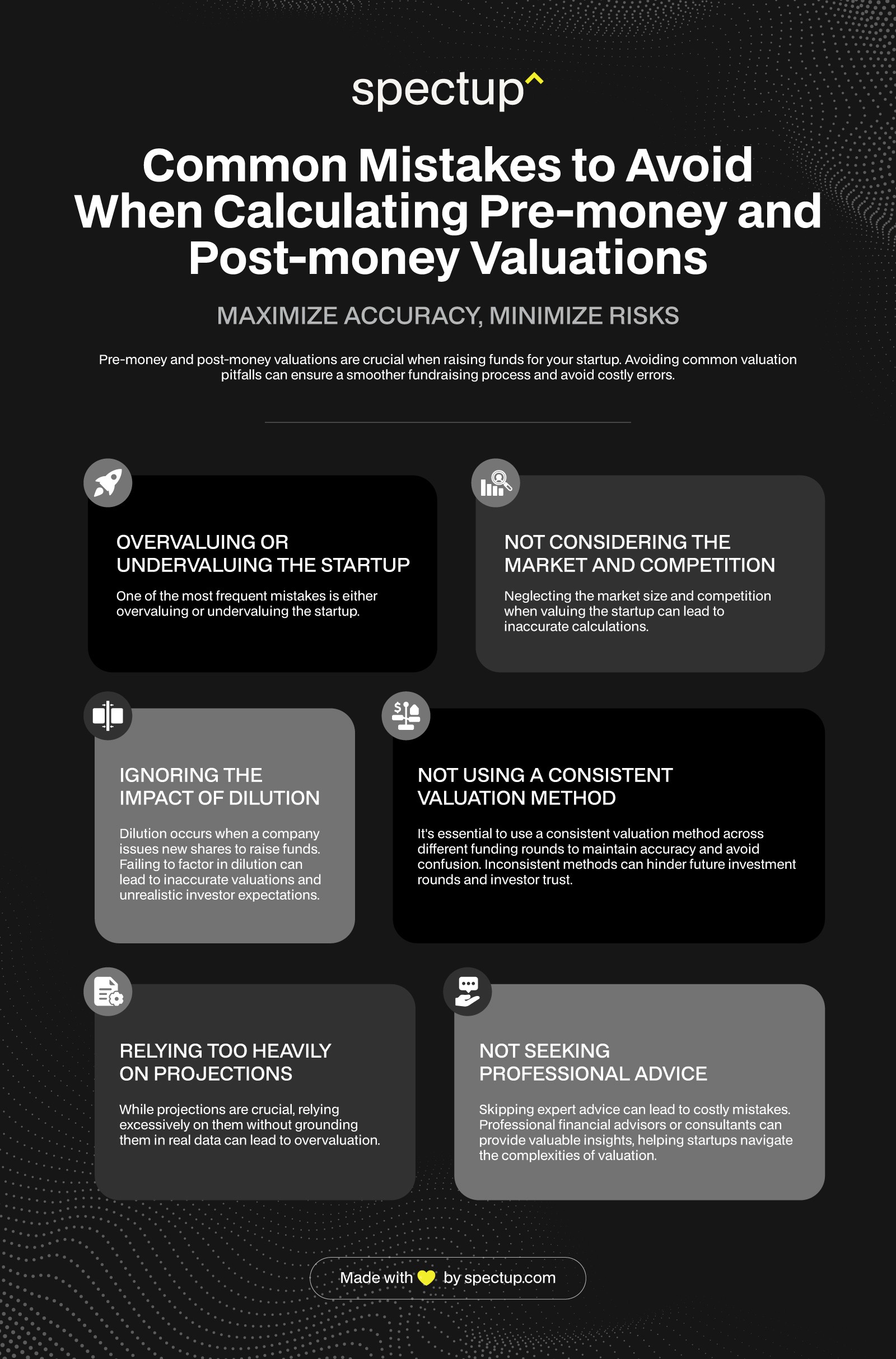
What are Some Common Mistakes to Avoid when Calculating Pre-money and Post-money Valuations?
While pre-money and post-money valuations are crucial for startups to raise funds, several common mistakes can be avoided. Here are some of the most common mistakes to watch out for when calculating pre-money and post-money valuations:
While pre-money and post-money valuations are crucial for startups to raise funds, several common mistakes can be avoided. Spectup helps avoid common valuation mistakes by providing accurate data, clear methodologies, and expert guidance for pre-money and post-money calculations.
Here are some of the most common mistakes to watch out for when calculating pre-money and post-money valuations:
Overvaluing or undervaluing the startup
One of the most common mistakes startups make when calculating pre-money and post-money valuations is overvaluing or undervaluing their business. Overvaluing the startup can make the investment opportunity less attractive to investors, while undervaluing the business can result in the startup receiving less funding than it needs.
Not considering the market and competition
Another common mistake is not considering the market and competition when calculating pre-money and post-money valuations. Startups must take into account the size of the market they are targeting and the competition they face. This information can help them determine a more accurate valuation and identify potential risks and opportunities.
Ignoring the impact of dilution
Dilution occurs when a startup issues new shares to raise funds. This can result in the ownership percentage of existing stockholders being reduced. Ignoring the impact of dilution when calculating pre-money and post-money valuations can result in inaccurate valuations and misaligned expectations among investors and stockholders.
Not using a consistent valuation method
Using the same valuation method consistently is crucial when calculating pre-money and post-money valuations. This ensures that the startup is being valued accurately and consistently over time. Using different valuation methods can result in inconsistent valuations and may make it difficult to attract investors for future funding rounds.
Relying too heavily on projections
Projections are an essential part of calculating pre-money and post-money valuations, but relying too heavily on them can be a mistake. Startups must ensure their projections are realistic and based on accurate data. Overly optimistic projections can result in overvaluing the startup and may lead to financial instability in the future.
Not seeking professional advice
Finally, not seeking professional advice when calculating pre-money and post-money valuations can be a costly mistake. Working with experienced financial modeling consultants can help startups avoid common mistakes and ensure their valuations are accurate and attractive to investors.
How Pre-Money and Post-Money Valuations Impact a Startup's Ability to Raise Future Funding Rounds
Pre-money and post-money valuations can significantly impact a startup's ability to raise future funding rounds. A higher valuation means that the startup is worth more, which can attract more potential investors.
However, it also means that the startup will need to offer a larger equity stake to investors, potentially diluting the ownership percentage of current stockholders.
Startups with a high pre-money valuation may struggle to attract investors for the next funding round. This is because investors expect a higher return on investment for a startup that is valued at a higher price. Meanwhile, a low pre-money valuation may make it easier for a startup to attract investors as they may see it as undervalued and a chance to get a high return on investment.
Yet, a low pre-money valuation can also signal that a startup is struggling, which can make it challenging to secure future funding rounds. Post-money valuations can also impact a startup's ability to raise funding. A high post-money valuation makes it difficult to raise additional funding rounds, while a low one can make it easier to attract investors.
To successfully secure funding for a startup, it's important to have a well-planned investor outreach plan in place. This includes understanding the difference between pre-money and post-money valuations and being able to accurately represent the startup's financial worth to potential investors.
Examples of Successful Startups That Used Pre-Money and Post-Money Valuations to Their Advantage
Many successful startups have used pre-money and post-money valuations to their advantage. Here are some examples:
Uber: In 2010, Uber had a pre-money valuation of $4 million. In 2014, it had a post-money valuation of $18.2 billion. This increase in valuation helped Uber secure funding and become one of the most successful startups of all time.

Airbnb: In 2009, Airbnb had a pre-money valuation of $1.3 million. In 2017, it had a post-money valuation of $31 billion. This increase in valuation helped Airbnb secure funding and become one of the most successful startups in the hospitality industry.

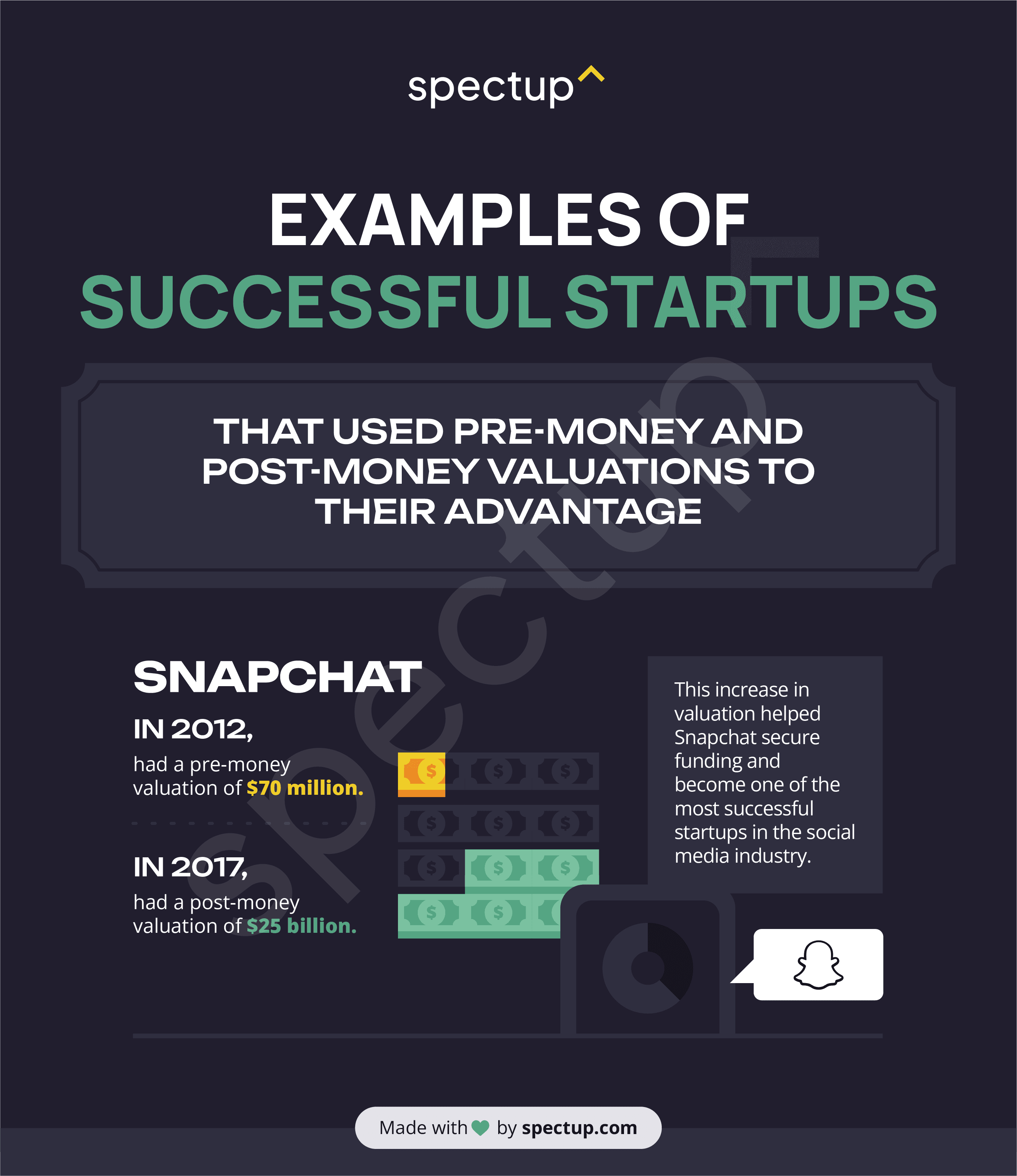
Snapchat: In 2012, Snapchat had a pre-money valuation of $70 million. In 2017, it had a post-money valuation of $25 billion. This increase in valuation helped Snapchat secure funding and become one of the most successful startups in the social media industry.
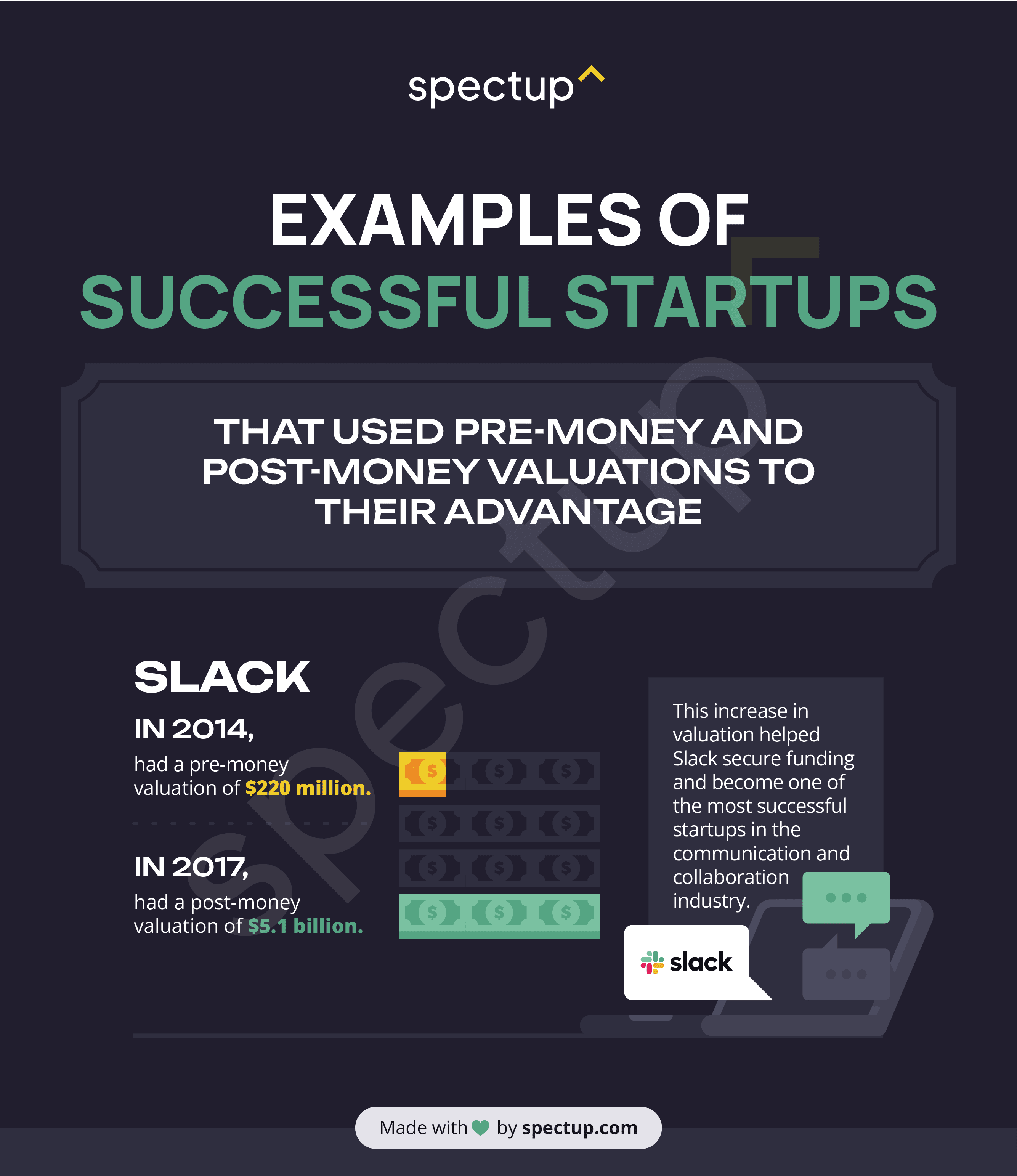
Slack: In 2014, Slack had a pre-money valuation of $220 million. In 2017, it had a post-money valuation of $5.1 billion. This increase in valuation helped Slack secure funding and become one of the most successful startups in the communication and collaboration industry.
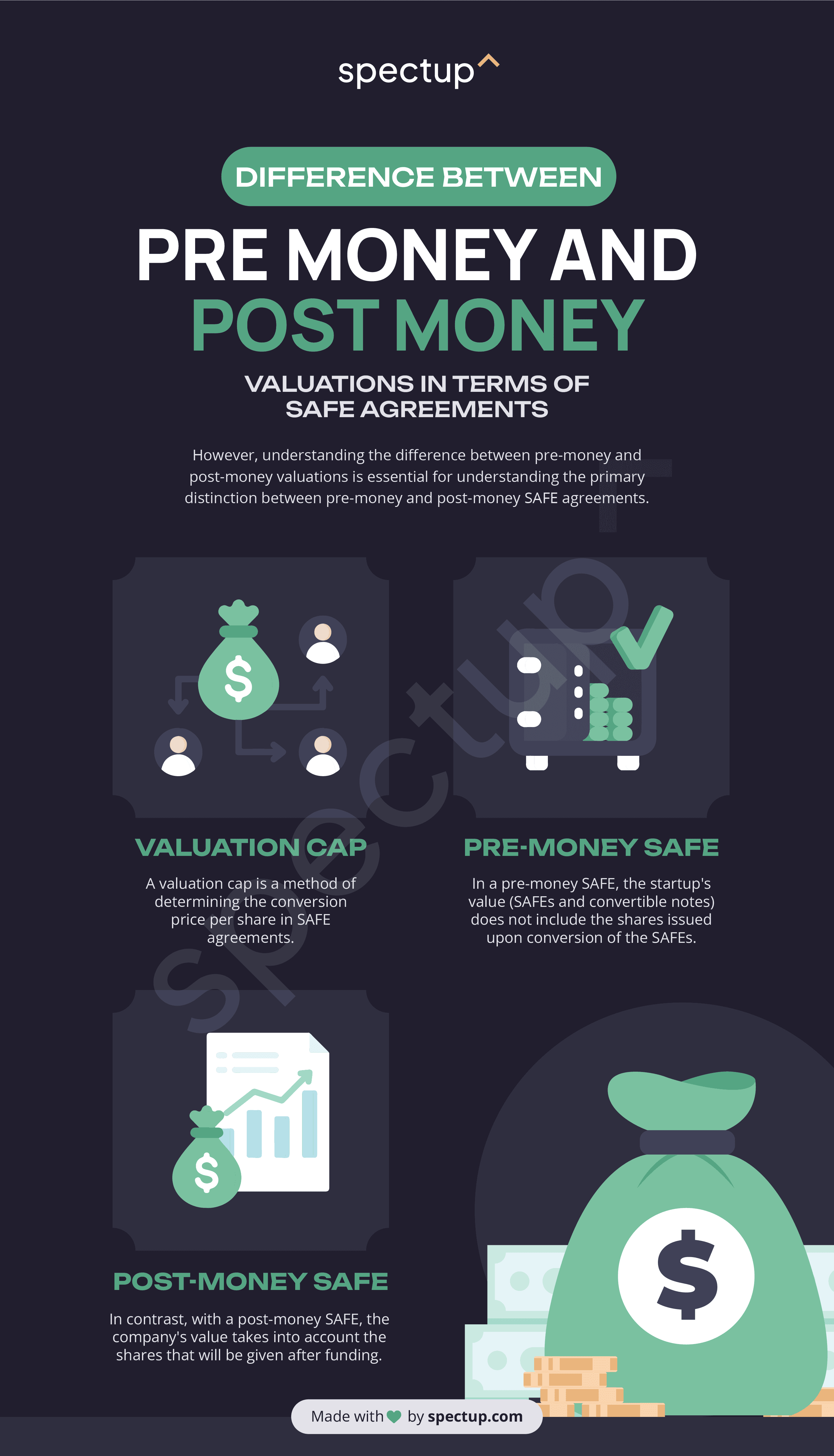
Difference between Pre Money and Post Money Valuations in Terms of SAFE Agreements
A Simple Agreement for Future Equity (SAFE) is a mutual agreement between the investor and the startup, which allows investors to invest in early-stage startups without determining a valuation upfront. SAFE agreements are a popular method for raising funds for startups because they are simpler and faster than traditional equity financing rounds.
However, understanding the difference between pre money vs post money valuations is essential for understanding the primary distinction between pre-money and post-money SAFE agreements.
Valuation Cap
A valuation cap is a method of determining the conversion price per share in SAFE agreements. The conversion price is the price that the investor would pay for each share upon conversion of the SAFE. The valuation cap sets a maximum price at which the convertible security will convert into equity.
Pre-Money SAFE
In a pre-money SAFE, the startup's value (SAFEs and convertible notes) does not include the shares issued upon conversion of the SAFEs. The pre-money SAFE calculates the conversion price per share based on firm capitalization without incorporating the shares to be issued following SAFE conversion.
This means that the ownership of earlier investors will be diminished with each subsequent investment. Pre-money SAFEs can be advantageous to startup entrepreneurs as they enable them to obtain pre-valuation funding similar to a convertible note.
Post-Money SAFE
In contrast, with a post-money SAFE, the company's value takes into account the shares that will be given after funding. The shares that will be issued upon conversion of SAFEs are already accounted for in the company's capitalization. As a result, it ensures that shareholders, rather than SAFE holders or investors, bear the cost of ownership percentage dilution.
Summing Up
Pre-money and post-money valuations are key terms in equity financing. Pre-money valuation is the value of your startup before investment, while post-money valuation is the value after the investment. These terms differ in timing, affecting your ownership dilution as a founder.
Knowing the difference pre money vs post money helps you negotiate better with angel and venture capital investors. Understanding pre-money vs post-money valuations will guide you on how much dilution to expect with each funding round and how to value your startup accurately.
Looking for help for your startup? spectup offers essential guidance and support for entrepreneurs and venture capital professionals at every stage of financing and growth. Let us help strengthen your team as you bring your new product to market.
Niclas Schlopsna
Partner
Ex-banker, drove scale at N26, launched new ventures at Deloitte, and built from scratch across three startup ecosystems.








